With most people suffering from back pain at some point of time in their lives, researchers have now developed a digital test to measure the functioning of the spine.
With a digital spine analysis (DSA), a muscular evaluation of the spine, India’s Qi Spine Clinic generated a spine function graph that led to customised treatment and non-surgical therapy for many spine specialists, Qi claimed.
“It is really simple. The diabetes doctor wants to know your blood sugar levels. The cardiologist wants to know your blood pressure (BP) and your angiogram,” said Nithij Arenja, promoter, Qi Spine Clinic.
“What can be measured, can be managed. We generate a Spine Function Graph which provides a vital link to the treatment of your spine function,” Nithij added.
The spine is the least measured and most miraculous engineering marvel in our body, Nithij noted.
“From bankers to housewives, young college students to sportsmen, Qi has seen every conceivable patient category,” said Garima Anandani, head of spine consultants at Qi.
“The problems are all different, and hence the therapy is different for each person too,” Anandani added.
Traditional scanning methods such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and X-rays fail to identify a clear cause for back pain in 85 percent of the cases, a statement from the clinic added.
Source: Business standard


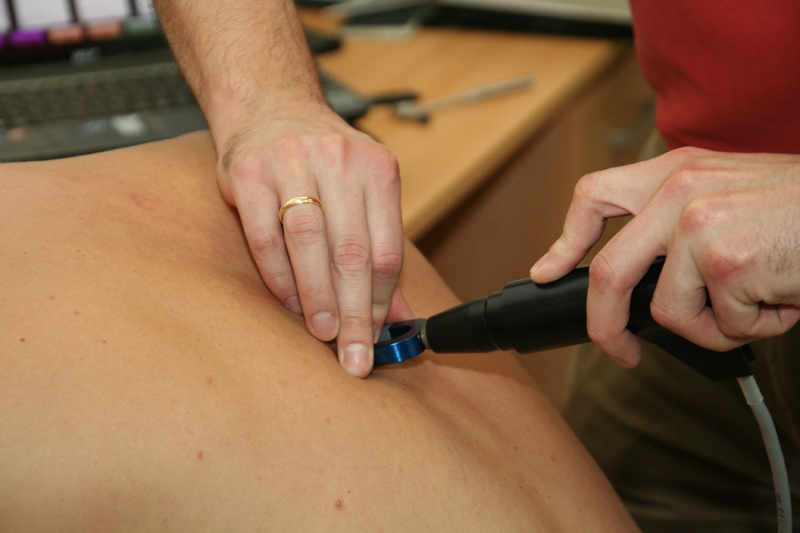
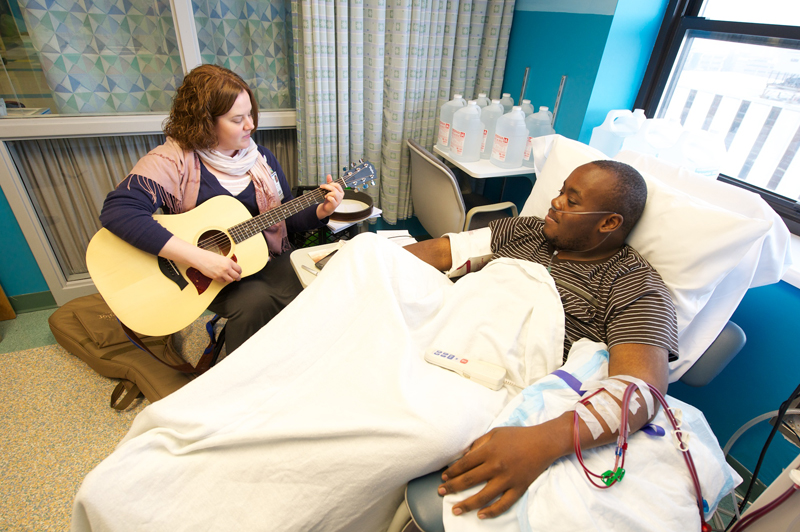

 A new study has revealed that low back pain causes more work disability around the globe than any other condition.
A new study has revealed that low back pain causes more work disability around the globe than any other condition.



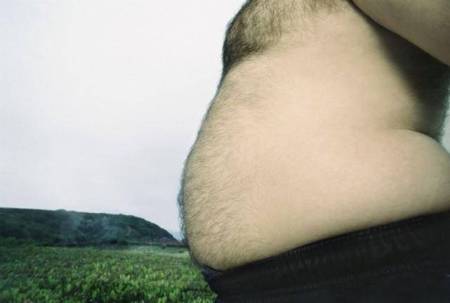 High waist circumference, severe obesity has been linked with the greatest risk of death in heart attack survivors, according to a research.
High waist circumference, severe obesity has been linked with the greatest risk of death in heart attack survivors, according to a research.