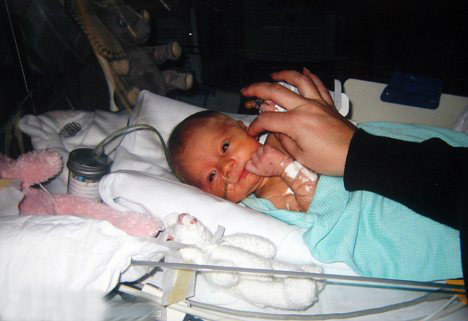
A baby girl, who was diagnosed with a life threatening congenital heart disease in the womb, got a new lease of life as doctors at a city hospital performed a corrective surgery on her two hours after she was born.
Doctors at Care Hospital said the girl was suffering from a rare disorder wherein the oxygen-rich blood returned from the pulmonary veins was abnormally getting diverted to the liver instead of heart.
“A foetus is dependent on mother’s blood and hence the baby was normal in the womb. But after birth, babies suffering from this rare malformation, referred as Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR), die without a reconstructive surgery,” said Dr K Nageshwar Rao, paediatric cardiologist, Care Hospital, and part of the team that performed the first-of-its-kind surgery.
Source: Healcon