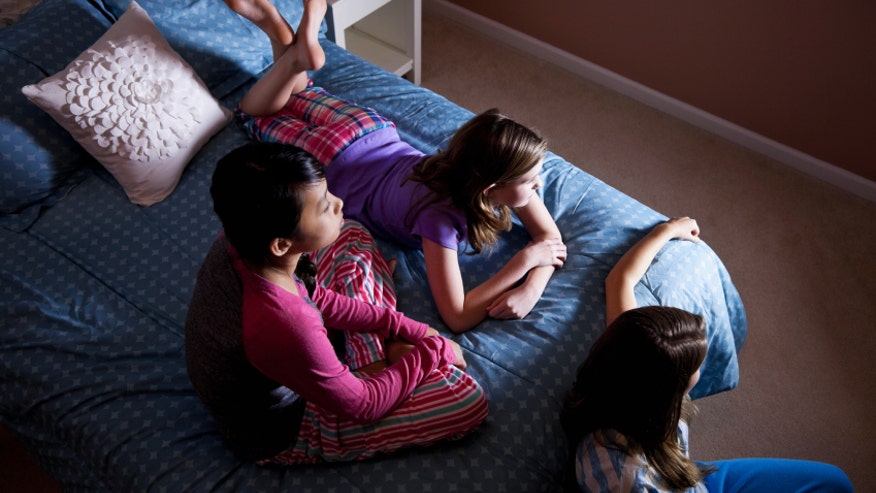

In another blow to kids’ pleas to watch more television before bed, a new study suggests increased TV time is linked to less sleep. What’s more, black, Latino and other minority children slept less when they had TV sets in their bedrooms.
“Inadequate sleep in childhood is associated with health outcomes, including attention problems, school performance and an increased risk of obesity,” Elizabeth Cespedes told Reuters Health. Cespedes is the study’s lead author from the Harvard School of Public Health in Boston.
“We wanted to know if television viewing may be associated with shorter sleep duration in children,” she said. For the new report, she and her colleagues used data from an existing study of mothers and children who lived in the Boston area. The study included 1,864 children who were born between 1999 and 2003. Mothers reported how much television their child watched at six months old and then every year until age seven.
Mothers also reported whether children slept with a television in their bedroom every year starting midway through the study.
The average time children slept each day decreased from about 12 hours at six months to about 10 hours at seven years, and total TV viewing increased from about one hour per day to 1.6 hours.
The proportion of children who slept with a TV in their bedroom increased from 17 percent to 23 percent between ages four and seven years, too. Children typically sleep less as they get older, the researchers noted. Still, each extra hour of TV watching added to their lifetime average was tied to a seven-minute decrease in daily sleep.
That association was stronger for boys than girls, according to findings published in Pediatrics. “I think in our case it’s possible that the content of the television watched may be different for boys than girls,” Cespedes said. “The content may be especially disruptive.”
She and her colleagues also found that sleeping with a TV in the bedroom was tied to 31 fewer minutes of sleep per day among racial and ethnic minority children. The effect of a TV in the bedroom was not as strong among white, non-Hispanic children.
Cespedes said it’s hard to know why minority children would be more affected by having a TV in the bedroom. “At all time points, racial and ethnic minority children in our study were sleeping a bit less and watching more television,” she said.
Dr. Heidi Connolly, a sleep specialist who was not involved with the new study, said the research is one of several recent papers that point toward a negative effect of TV on sleep.
“This doesn’t seem like very much, but if you think about it, seven minutes every night by the time you get to the end of the week you’re already a half hour short on sleep,” Connolly, from the University of Rochester Medicine’s Golisano Children’s Hospital in New York, said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends against children younger than two years old watching any television. It also recommends limiting older children’s screen time to no more than one or two hours per day.
“I think it’s unreasonable to expect that kids aren’t going to watch TV,” Connolly told Reuters Health. “It’s pervasive in our culture. But you do want to limit screen time to less than two hours per day.” Connolly also said people sometimes say their children need the TV on to sleep, but that’s not the case.
She said consistent bedtimes, regular bedtime routines and a TV-free comfortable sleeping environment are good sleep behaviors.
Source: orlando sentinel









 High waist circumference, severe obesity has been linked with the greatest risk of death in heart attack survivors, according to a research.
High waist circumference, severe obesity has been linked with the greatest risk of death in heart attack survivors, according to a research.